Author: Manuel J. Arroyo Pulgar
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) just released the 2019 Antibiotic Resistance Threats Report in the United States. It includes statistics about infection due to resistant microorganisms in the U.S., an updated threats list about new antibiotic resistances and a lot of interesting complementary information about this worldwide problem, such as the mechanisms by which microorganisms acquire the antimicrobial resistance or how antibiotic resistance spreads around the world.
The report indicates that more than 2.8 million antibiotic-resistant infections occur in the U.S. each year, and more than 35,000 people die as a result. With these statistics it is understandable that the responsible authorities around the world are putting the spotlight on promoting actions to prevent, diagnose and treat these infections.
In addition, the report lists 18 antibiotic-resistant bacteria and fungi into three different categories based on level of concern to human health: urgent, serious and concerning. Some of these microorganisms are the carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter, Clostridioides difficile, ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae family, vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus or multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa among other.
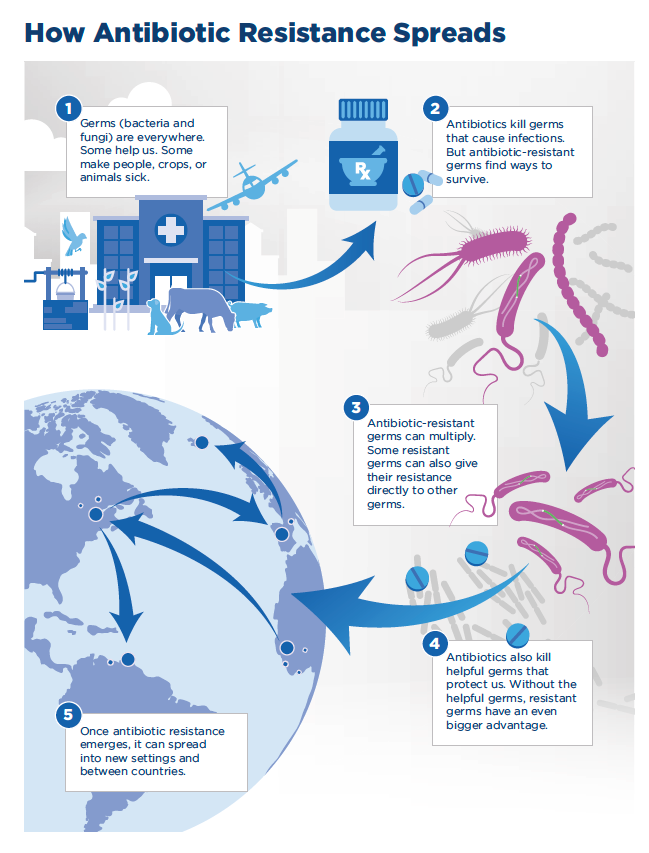
This report, just like other authorities, puts special interest in highlighting the importance of a good diagnosis, comparing this fact even with the antibiotics. Quoting the report, Diagnostics can be just as critical for fighting infections as antibiotics, and this is a fundamental part of the Clover Biosoft philosophy. We strongly believe that appropiarte treatment and prevention of antibiotic-resistant infections relies on diagnostic tools to detect these germs as soon as they emerge. Identifying correctly the resistance allows healthcare providers to use effective antibiotics and implement infection control measures to prevent spread.
Following the report, diagnostic tools can:
- Improve the accuracy and speed of a patient’s diagnosis, improving appropiate antibiotic selection and reducing unnecessary antibiotic use.
- Identify when germs spread, so that infection prevention and control can improve.
- Support public health tracking to rapidly identify threats and infection trends, informing public health response.
Finally, but not less important, the CDC report stands out the importance and the role of all researchers in this area which are needed to research and improve diagnostic tests and the data they generate.
Remember that you can find more information and the full PDF report in the CDC’s website (cdc.fov).
REFERENCES:
https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/Biggest-Threats.html
